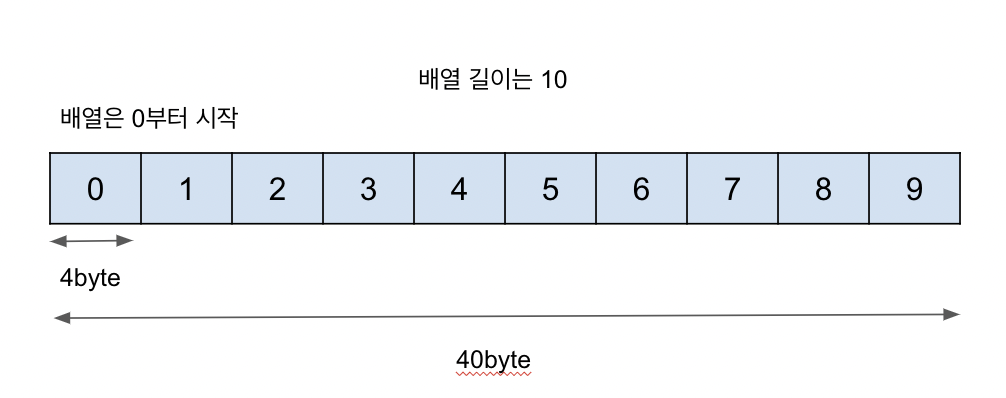
배열
동일한 자료형이 순차적으로 존재할 때 관리하기에 용이하다. 배열은 연속된 자료구조이다. 중간의 값을 지우게 되면, 뒤의 값들이 앞으로 땡겨오게 된다.
** 배열은 인덱스(순서)는 0부터 시작한다.
배열 선언 방법
자료형[] 배열이름 = new 자료형[갯수]; ex) int[] intArr = new int[10];
자료형 배열이름[] = new 자료형[갯수]; ex) int intArr[] = new int[10];
public class ArrayMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int as[];
int[] b;
as = new int[3];
as[0] = 1;
as[1] = 2;
as[2] = 3;
for (int a : as) {
System.out.println(a);
}
int[] months = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
}
}
값을 넣어줄 때는 아래와 같이 각 인덱스별로 값을 할당하여 준다.
** 변수명.length를 통해 해당 배열의 크기를 알 수 있다.
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] intArr = new int[3];
intArr[0] = 1;
intArr[1] = 2;
intArr[2] = 3;
for (int i=0; i < intArr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(intArr[i]);
}
}
}배열 선언과 동시에 초기화
배열의 선언과 동시에 초기화 하는 경우에는 배열의 갯수를 명시하지 않는다. 초기화시 갯수를 명시하는 경우 에러가 날 수 있다.
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] intArr = new int[] {1, 2, 3};
// 아래와 같이 갯수를 명시하면 에러가 발생한다.
// int [] intArr = new int[3] {1, 2, 3};
int [] intArr2 = {1, 2, 3};
}
}초기화 하지 않고 선언만 하는 경우 정수는 0, 실수는 0.0, 객체는 null로 초기화된다.
package arrayTest;
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] num = new double[5];
int size = 0;
num[0] = 10.0; size++;
num[1] = 20.0; size++;
num[2] = 30.0; size++;
double lengthTotal = 1;
double sizeTotal = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
System.out.println(num[i]);
lengthTotal *= num[i];
// 10.0
// 20.0
// 30.0
// 0.0
// 0.0
// length하면 총배열의크기인 5만큼 반복하며 배열에서 할당되지 않은 부분은 0.0으로 초기화되어 값이 0이 된다.
}
System.out.println("length total ===> "+lengthTotal);
//size를 이용하여 총 배열의 크기가 아닌 실제 값이 할당된 크기만큼만 반복되도록 할 수 있다.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++ ) {
System.out.println(num[i]);
sizeTotal *= num[i];
// 10.0
// 20.0
// 30.0
}
System.out.println("size total ===> "+sizeTotal);
}
}배열에 문자를 담는 경우
public class CharArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] alphabets = new char[26];
char ch = 'A'; // 65
// char 타입의 변수에는 ''(작은따옴표)를 이용하여 하나의 문자를 저장할 수 있다.
// ""를 사용시 에러가 난다.
for (int i = 0; i < alphabets.length; i++, ch++) {
alphabets[i] = ch;
System.out.println(alphabets[i]);
}
}
}배열안에 객체 담기
배열명[index] = new 클래스명(); ex) library[0] = new Book("태백산맥1","조정래1");
배열안에 들어갈 객체 요소
public class Book {
private String bookName;
private String author;
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public Book() {}
public Book (String bookName, String author) {
this.bookName = bookName;
this.author = author;
}
public void showBookInfo() {
System.out.println(bookName + "," + author);
}
}실제 배열 부분
public class ObjArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] library = new Book[5];
for (int i=0; i< library.length; i++) {
System.out.println(library[i]);
}
library[0] = new Book("태백산맥1","조정래1");
library[1] = new Book("태백산맥2","조정래2");
library[2] = new Book("태백산맥3","조정래3");
library[3] = new Book("태백산맥4","조정래4");
library[4] = new Book("태백산맥5","조정래5");
for (int i=0; i< library.length; i++) {
System.out.println(library[i]);
library[i].showBookInfo();
}
}
}배열 복사
System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length);
System.arraycopy는 자바에서 제공하는 배열 라이브러리이다.
- src : 복사할 배열명
- srcPos : 복사할 배열의 첫 번째 위치
- dest : 복사해서 붙여 넣을 대상 배열명
- destPos : 복사해서 대상 배열에 붙여넣기 할 첫 번째 위치
- length : 복사하려는 갯수
package arrayTest;
public class ArrayCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int[] arr2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 2, 2);
// arr1의 첫번째 요소부터 2개를 arr2의 3번째 요소 즉 인덱스는 2에서부터 붙여넣기 하겠다.
for(int i = 0; i< arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
}
// 1
// 2
// 10
// 20
// 5
}
}객체 배열 복사
// 얕은 복사 - 배열의 주소를 복사하는 것으로, 복사한 배열(원본)의 값이 변경되면 복사된 배열(복사본)의 값도 변경된다.
// 깉은 복사 - 배열의 값 자체를 복사하는 것이다. 복사한 배열(원본)의 값이 변경되어도 복사된 배열(복사본)의 값은 변경되지 않는다.
** 객체 자체를 아예 new 로 새롭게 할당하여 준 경우에는 복사된 배열의 값이 변경되지 않는다.
public class CopyObj2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] bookArr1 = new Book[3];
Book[] bookArr2 = new Book[3];
Book[] bookArr3 = new Book[3];
bookArr1[0] = new Book("태백산맥1","조정래1");
bookArr1[1] = new Book("태백산맥2","조정래2");
bookArr1[2] = new Book("태백산맥3","조정래3");
bookArr3[0] = new Book();
bookArr3[1] = new Book();
bookArr3[2] = new Book();
// 깉은 복사의 경우 => 값 자체를 복사 =====================
for (int i = 0; i < bookArr3.length; i++) {
bookArr3[i].setBookName(bookArr1[i].getBookName());
}
// 얕은 복사의 경우 => 값이 저장된 주소를 복사 ===============
System.arraycopy(bookArr1, 0, bookArr2, 0, 3);
bookArr1[1] = new Book("new 태백산","조정래");
bookArr1[2].setBookName("new new 태백산맥");
// 원본값 =========================================
for (int i = 0; i<bookArr1.length; i++) {
bookArr1[i].showBookInfo();
}
// 태백산맥1,조정래1
// new 태백산맥,조정래1
// new new 태백산맥,조정래1
// 깉은 복사의 경우 => 값 자체를 복사하여 복사된 값의 변경이 없
for (int i = 0; i < bookArr3.length; i++) {
System.out.println(bookArr3[i].getBookName());
}
// 얖은 복사의 경우 => 값 주소를 복사하였기 때문에, 원본 주소에 저장된 값이 변경됨에 따라 복사된 값도 변경됨.
for (int i = 0; i<bookArr2.length; i++) {
bookArr2[i].showBookInfo();
}
// 태백산맥1,조정래1
// 태백산맥1,조정래1
// new new 태백산맥,조정래1
}
}- 얕은 복사
public class ArrayMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[5];
int[] b = a;
b[0] = 5;
// a[0]의 값도 5가 된다.
}
}- 깊은 복사 , Arrays.copyOf() 활용
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[5];
int[] copy = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length);
copy[0] = 5;
// a는 copy의 값에 영향을 받지 않는다.
// 배열의 크기를 늘릴 수 도 있다.
int[] copyDoubleSize = Arrays.copyOf(a, 2*a.length);
}
}- Arrays.sort()
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2, 5, 4, 7, 3 };
Arrays.sort(a);
for(int ele: a) {
System.out.println(ele);
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
// 7
}
}
}** 향상된 for 문
for (자료형 변수 : 배열명 ) { };
public class UpdatedFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] strArr = {"java", "javascript", "c", "go", "rust"};
for (String ele: strArr) {
// ele는 배열의 요소를 의미한다.
// 배열의 총 길이만큼 배열 요소를 순회한다.
System.out.println(ele);
}
// java
// javascript
// c
// go
// rust
}
}다차원배열
2차원 이상의 배열을 의미한다.
자료형[][] 배열명 = new 자료형 [(행)갯수][(열)갯수];
public class UpdatedArr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] newArr1 = new int[2][3];
// 다차원배열 선언과 동시에 초기
int[][] newArr2 = {{1,2,3}, {4,5,6}};
for(int i = 0; i < newArr2.length; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < newArr2[i].length; j++) {
System.out.println(newArr2[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("");
}
char[][] alphabets = new char[13][2];
char ch = 'A';
for (int i = 0; i < alphabets.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < alphabets[i].length; j++) {
alphabets[i][j] = ch++;
System.out.println(alphabets[i][j]);
}
}
}
}ArrayList
배열 관련하여 편리한 메서드를 제공하여 주는 클래스이다.
** ArrayList에서는 index 연산자를 제공하지 않는다. 때문에 ArrayList를 사용한 경우 index를 통해 접근할 수 없다.
ArrayList<자료형(E)> 배열명 = new ArrayList<E>();
주요메서드
- boolean add(E e) -> 요소하나를 배열에 추가하여 준다. E는 요소의 자료형을 의미한다.
- int size() -> 배열에 추가된 요소 전체 갯수를 반환한다.
- E get(int index) -> 배열의 index 위치에 있는 요소값 반환
- E remove(int index) -> 배열의 index위치에 있는 요소를 제거하고, 제거된 값을 반환
- boolean isEmpty() -> 배열이 비어있는지 확인
** arrayList docs: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/ArrayList.html
ArrayList (Java Platform SE 8 )
Resizable-array implementation of the List interface. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements, including null. In addition to implementing the List interface, this class provides methods to manipulate the size of the array that is
docs.oracle.com
예시
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<int[]> intList = new ArrayList<int[]>();
strList.add("aaa");
strList.add("bbb");
strList.add("ccc");
for (int i = 0; i < strList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(strList.get(i));
}
String c = strList.remove(2);
System.out.println(c);
// ccc
System.out.println(strList);
// [aaa, bbb]
String b = strList.remove(1);
System.out.println(b);
// bbb
System.out.println(strList);
// [aaa]
String a = strList.remove(0);
System.out.println(a);
// aaa
System.out.println(strList);
// []
System.out.println(strList.isEmpty());
// true
}
}subject 클래스
public class Subject {
private String name;
private int scorePoint;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getScorePoint() {
return scorePoint;
}
public void setScorePoint(int scorePoint) {
this.scorePoint = scorePoint;
}
}
student 클래스 ~ 학생이 여러 과목을 수강할 수 있다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Student {
private int studentID;
private String studentName;
private ArrayList<Subject> subjectList;
public Student(int studentID, String studentName) {
this.studentID = studentID;
this.studentName = studentName;
subjectList = new ArrayList<Subject>();
}
public void addSubject(String name, int score) {
Subject subject = new Subject();
subject.setName(name);
subject.setScorePoint(score);
subjectList.add(subject);
}
public void showStudentInfo() {
int total = 0;
for(Subject ele: subjectList) {
total += ele.getScorePoint();
System.out.println("학생"+ studentName+"-"+ele.getName()+":"+ele.getScorePoint());
}
System.out.println("총 점수는: "+total);
}
}main 클래스
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentLee = new Student(1001, "Lee");
studentLee.addSubject("국어", 100);
studentLee.addSubject("수학", 90);
studentLee.showStudentInfo();
Student studentKim = new Student(1002, "Kim");
studentKim.addSubject("국어", 100);
studentKim.addSubject("수학", 90);
studentKim.showStudentInfo();
}
}
출처
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ Java ] - 상속과 다형성 (0) | 2022.09.04 |
|---|---|
| [ Java ] - 이클립스에서 디버깅 하는 법 (0) | 2022.09.04 |
| [ Java ] - 싱글턴(singleton) 패턴 (0) | 2022.09.03 |
| [ Java ] - 기초 예제 (대중 교통 관련) (0) | 2022.09.02 |
| [ JAVA ] - 프로젝트 생성 후 hello world 찍기 (0) | 2022.08.19 |